KONJAC
Indonesia has a source of raw materials for konjac with a total land area of 47,641 hectares which can produce 714,000 tons per year. therefore we make it an export commodity. Konjac is a plant native to Asia and can be processed into various forms such as food and pharmaceuticals.
Are you looking for a konjac product solution for industrial needs? We are here to answer all your needs
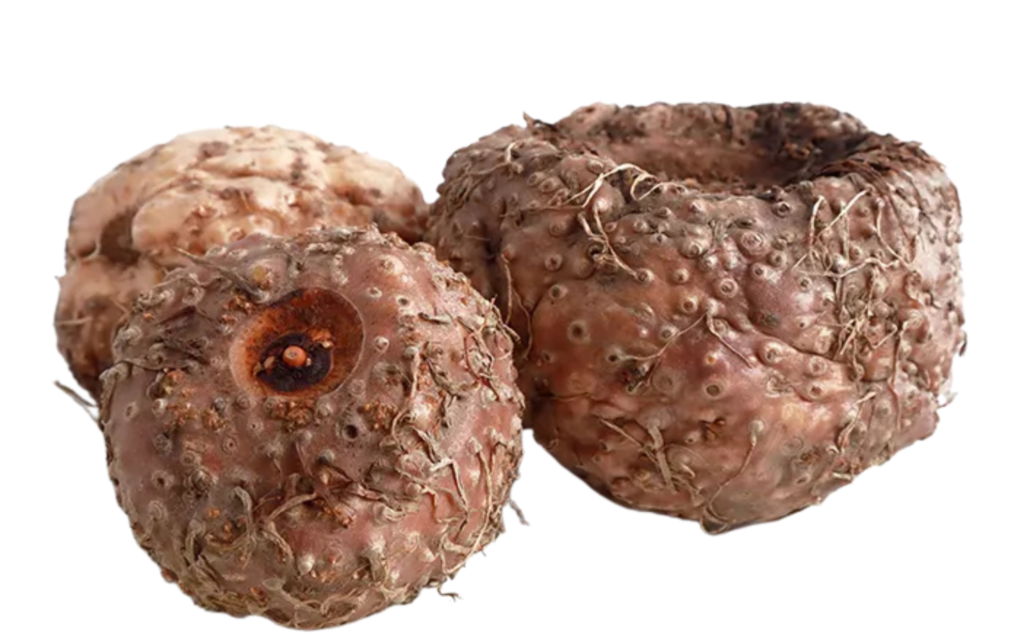
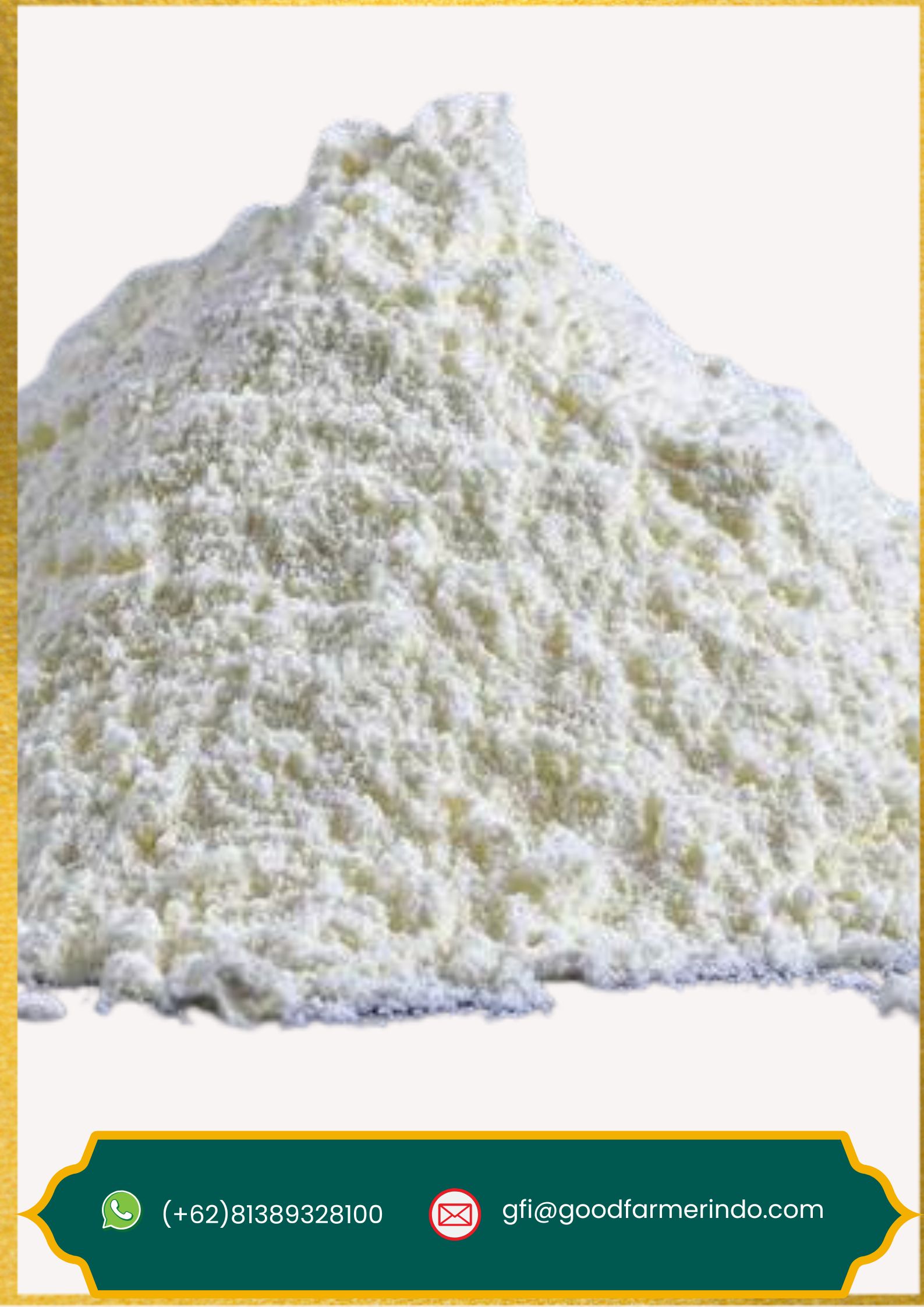


Konjac Flour
This flour is rich in glucomannan, a highly water-soluble dietary fiber and the main active component. Konjac flour is commonly used as a healthy food ingredient due to its low-calorie, gluten-free, and high-fiber properties. It has an excellent water-absorbing ability, allowing it to form gel-like or chewy textures.
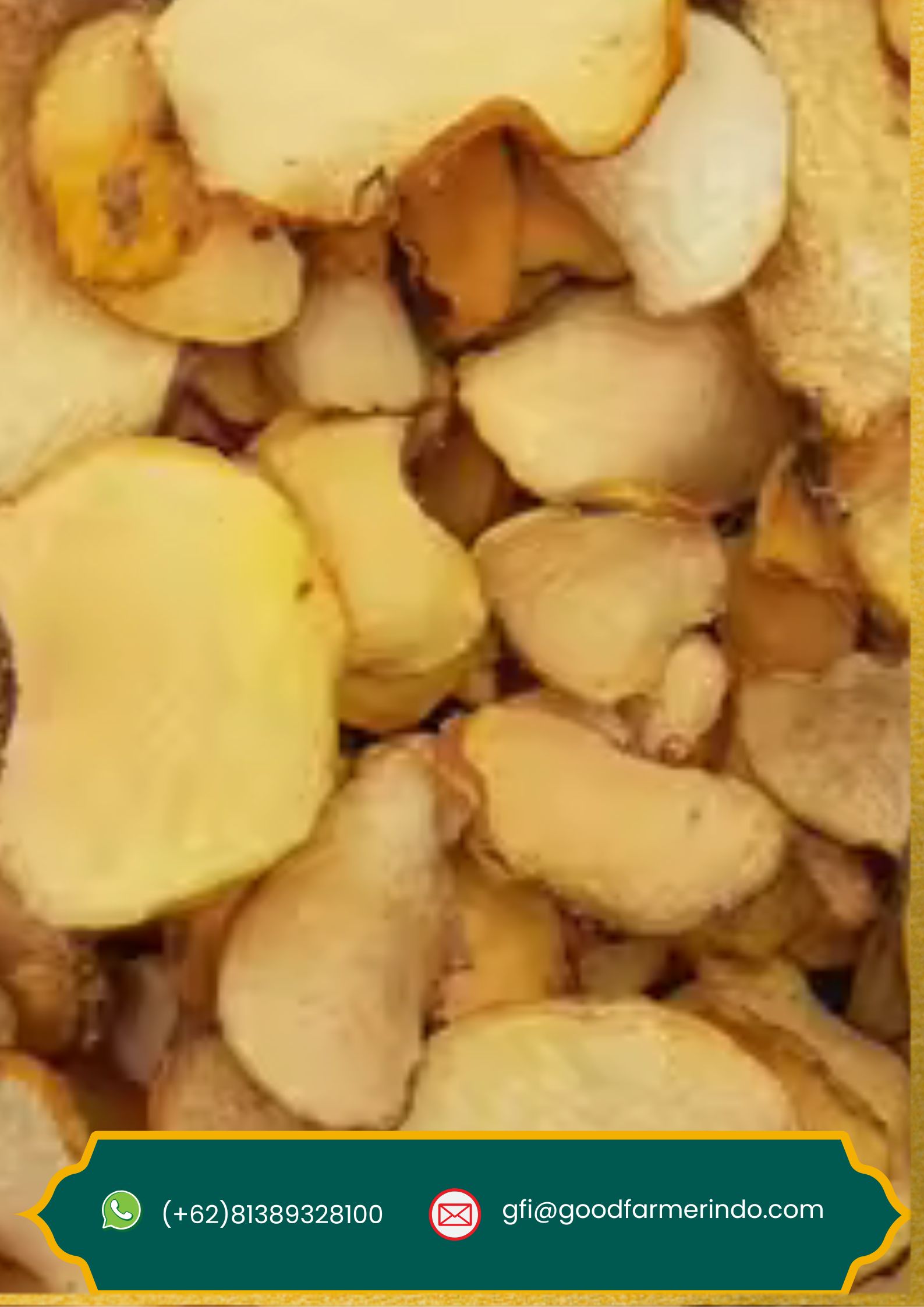

Konjac Chips
his product is a semi-finished raw material commonly used to produce various konjac-based products, such as konjac flour, shirataki noodles, jelly, and more. As it is still in its raw and unrefined form, konjac chips are typically used by food and pharmaceutical industries for further processing.
The Benefit Obtained From Konjac

Possesses viscous or food gelling properties.
.

Has a high water solubility of glucomannan.
.

It can be a healthy food because it has fiber and low calories.
.
Product Application

Vegan Meat
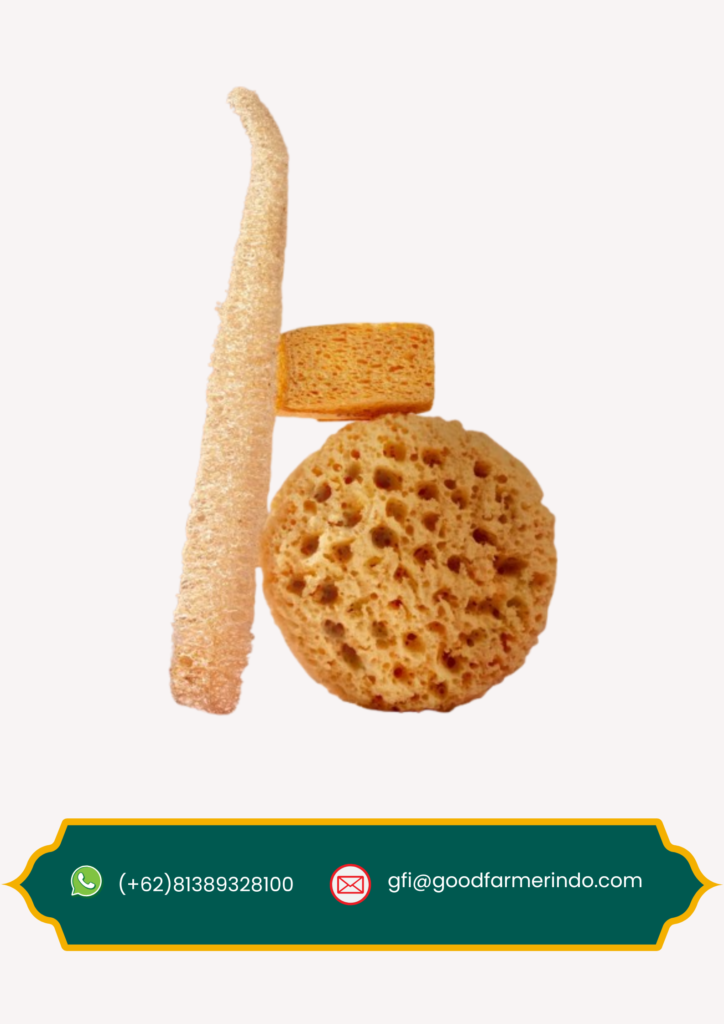

Sponge
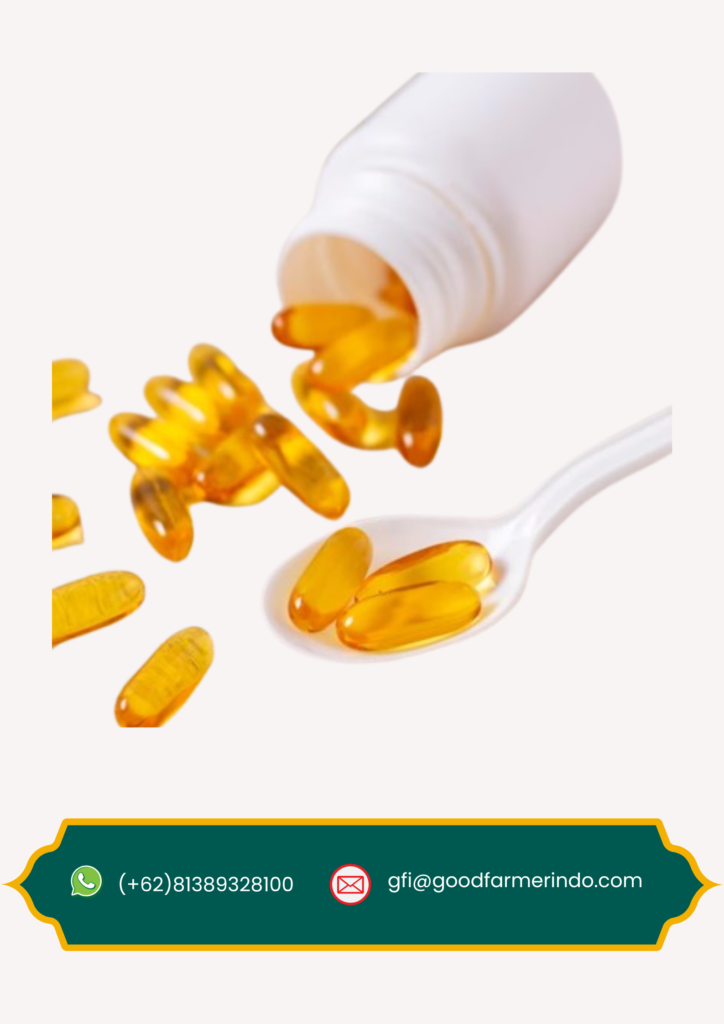

Dietary Supplement
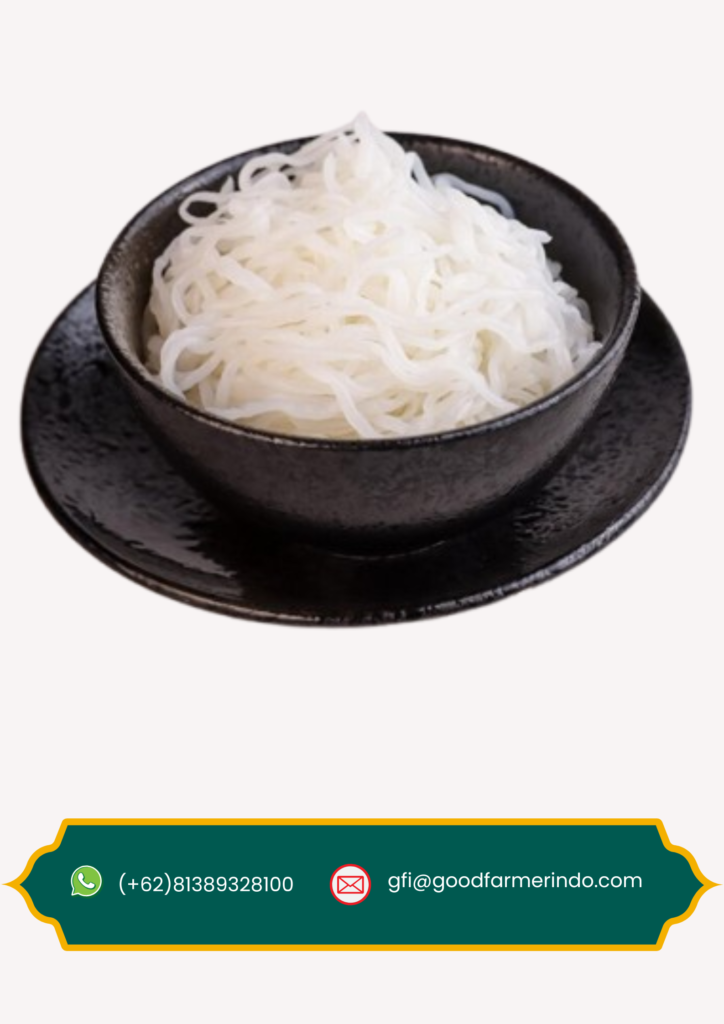

Shirataki

Boba

Noodle
How To Process It ?
1. Harvesting & Selection of Konjac Tubers
Process: Konjac tubers are hand-harvested at peak maturity (2-3 years) to ensure maximum glucomannan content.
Quality Control: Only fresh, defect-free tubers with uniform size are selected.
Traceability: Our farm-to-factory tracking ensures full transparency of raw material origins.
2. Washing & Peeling
Process: Tubers are pressure-washed with clean water to remove soil, then mechanically or manually peeled.
Sustainability: Closed-loop water systems minimize waste and environmental impact.
3. Slicing & Drying
Process: Tubers are cut into chips and dried via:
Sun-drying (for traditional products) or
Low-temperature dehydrators (to preserve glucomannan quality).
Output: Dried chips (~10% moisture content) ready for further processing.
4. Milling & Glucomannan Extraction
Process: Dried chips are ground into flour, then:
Further refined to extract pure glucomannan (if required).
Sieved for uniform particle size (80-200 mesh).
Quality Assurance: Lab-tested for glucomannan content, viscosity, and purity.
5. Value-Added Product Processing
Shirataki Noodles: Mixed with limewater, heated, and shaped.
Konjac Gel: Dissolved in water, heated, and cooled.
Food Additives: Natural thickener (E425).
6. Packaging & Sterilization
Process:
Vacuum-sealed or nitrogen-flushed packaging extends shelf life.
Preservative-free sterilization (UV/pasteurization).
Compliance: Meets international export standards (FDA, EU, Halal, etc.).
"Questions & Answers"
Questions That Are Always Asked ?
What is the definition of the konjac tuber plant?
The konjac tuber plant (Amorphophallus konjac) is a perennial herbaceous plant that has a large underground tuber. This tuber contains a high amount of glucomannan, a dietary fiber used to make konnyaku, noodles, and various other food products. Konjac is also known as the “voodoo lily” or “devil’s tongue” due to its large and striking foliage. The konjac tuber is round in shape, with a diameter that can reach up to 30 cm. It is a modified underground stem and contains a high level of starch.
Konjac leaves are large and spread out like an umbrella. The leaves can reach a height of about 1 meter and have dull pink-colored stalks. Konjac produces flowers on a spadix, which is protected by a dark purple bract (spatha).
Konjac is used as a food ingredient to produce noodles, konnyaku, and various other food items. Konjac flour is also used as a dietary supplement and as an ingredient in the food industry. Konjac is native to Yunnan in southwest China and is now cultivated in various countries across Asia.
What are the benefits of the konjac plant?
- Rich Source of Glucomannan Fiber
Konjac tubers are high in glucomannan, a water-soluble dietary fiber that supports digestion and helps lower cholesterol and blood sugar levels. - High Economic Value
Global demand for konjac products is steadily increasing, especially in Japan, Korea, China, and Western countries, making it a valuable export commodity. - Multi-Purpose Use (Food, Cosmetics, and Pharmaceuticals)
Konjac is used not only in food products (such as shirataki noodles and konnyaku) but also in cosmetics (like facial masks and cleansing sponges) and pharmaceuticals as a binder or gelling agent. - Low in Calories
Konjac-based products are very low in calories, making them ideal for weight-loss diets and popular among health-conscious consumers. - Can Grow in Marginal Land
Konjac can be cultivated in hilly or less fertile areas, making it suitable for farmers in remote regions. - Environmentally Friendly
Konjac farming is relatively eco-friendly, as it requires minimal chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
Is the konjac plant dangerous?
The konjac plant (Amorphophallus konjac) itself is not harmful, but it can become dangerous if not cooked properly or consumed in excessive amounts. The tuber contains calcium oxalate, which is toxic if eaten raw. Additionally, its high fiber content may cause digestive issues such as diarrhea, bloating, and gas.
1. Poisoning from Raw Consumption:
Konjac tubers contain calcium oxalate, which can cause poisoning if consumed raw.
However, when properly cooked, the calcium oxalate is removed, and the konjac tuber becomes safe to eat.
2. Side Effects of Overconsumption:
The high fiber content in konjac can lead to digestive problems such as diarrhea, bloating, and gas.
These symptoms may worsen in individuals with digestive conditions like Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS) or those taking anti-obesity medications.
Moreover, konjac can expand when mixed with water, which may pose a choking hazard if consumed in certain forms.
3. Benefits and Safety:
Konjac contains glucomannan, which can help with weight loss, relieve constipation, and lower cholesterol levels.
It also promotes digestive health due to its high fiber content.
However, it is important to consume konjac in moderation and be aware of potential side effects.
Can konjac be consumed?
Yes, konjac is safe to consume, but you need to pay attention to several things. Konjac is generally safe to consume in moderation and moderation. However, there are some risks to be aware of, especially in jelly or supplement form.
______________________________________________________________________________
Contact Us
- +(62)81389328100 (Marketing 1)
- +(62)81915011324 (Marketing 2)
- gf_indonesia13
- gfi@goodfarmerindo.com
